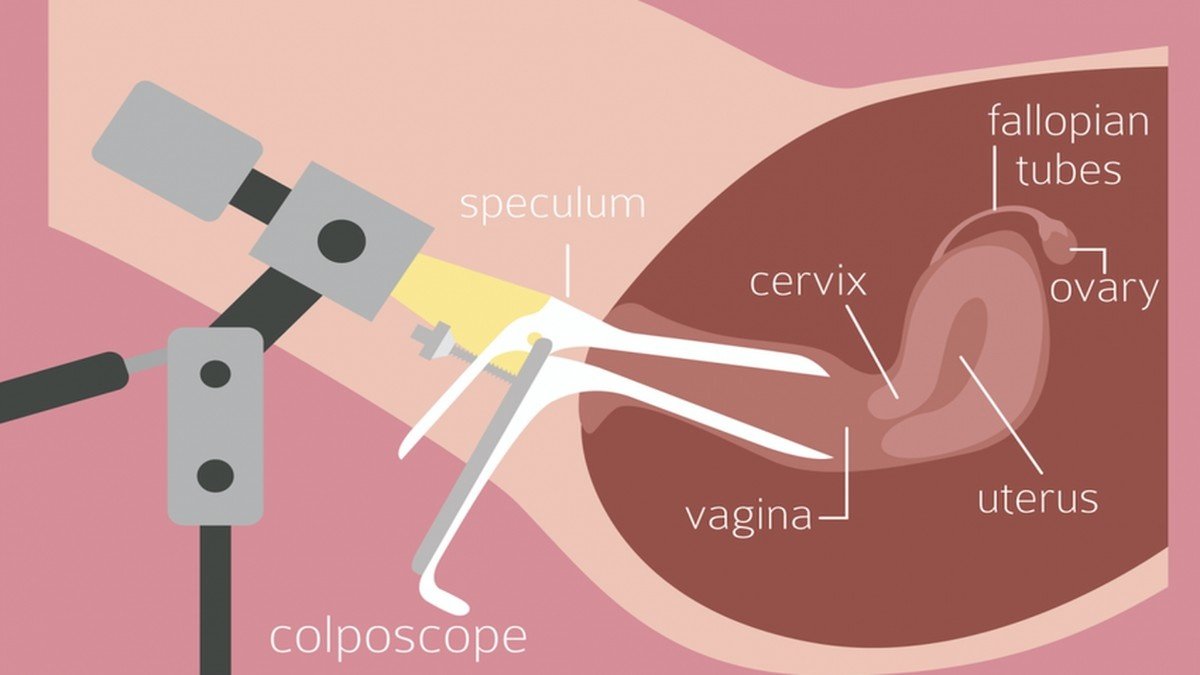
COLPOSCOPY
Colposcopy is a gynecological procedure used for examining the cervix, vagina, and vulva, often performed to evaluate abnormal Pap smear results or to further investigate symptoms such as abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain.
- Purpose: Colposcopy is performed to closely examine the cervical, vaginal, and vulvar tissues for signs of abnormalities, such as precancerous or cancerous lesions.
- Procedure Overview: During a colposcopy, the patient lies on an examination table with their feet placed in stirrups, similar to a pelvic exam. A speculum is inserted into the vagina to visualize the cervix, and a colposcope (a magnifying instrument) is used to examine the tissues more closely.
- Visualization of Tissues: The colposcope provides a magnified view of the cervix, allowing the healthcare provider to identify any abnormal areas. The healthcare provider may use a solution, such as acetic acid (vinegar), to help highlight abnormal tissues.
- Biopsy: If abnormal areas are identified during the colposcopy, the healthcare provider may take a biopsy (tissue sample) for further evaluation in a laboratory. This biopsy helps determine if the abnormality is precancerous or cancerous.
- Patient Comfort: Measures are taken to ensure the patient's comfort during the procedure, which typically takes only a few minutes to complete. Patients may experience mild discomfort similar to a Pap smear or pelvic exam.